Sex Disparity in Device Selection for CRT
Key findings
- The largest study of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) implants in the U.S. shows men were significantly more likely to undergo CRT therapy with an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) than women—despite predictors that indicate women demonstrate greater ICD efficacy
- Sexual disparity in implants increased significantly over the 7-year study period
- In an era of increasing clinical demand there is an urgent need for implant practices to improve alignment of device selection with those most likely to benefit
Women are significantly less likely than men to undergo cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) and to receive an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). This is true despite data showing female sex is consistently related to greater CRT efficacy and desired outcomes of reverse remodeling and improved survival. To understand why, an international team probed the largest publicly available all-payer inpatient health care database of CRT patient data in the U.S. (n= 311,009). Led by a team from Massachusetts General Hospital Corrigan Minehan Heart Center, their goal was to assess sex differences in CRT implant type, compare predictors of implant type and examine change over time in CRT device selection stratified by sex. The study sample included all adults greater than 18 years of age who received a CRT device between January 1, 2006 and December 31, 2012.
Subscribe to the latest updates from Cardiovascular Advances in Motion
Efficacy and Response Scores
The team used two morbidity scores previously shown to be associated with CRT and ICD efficacy. The ICD score comprised seven comorbidities associated with reduced ICD efficacy in HF patients: ischemic heart disease, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, chronic pulmonary disease, atrial fibrillation (AF), peripheral vascular disease and tobacco use. Score values were 0,1-2, > 3. At three or greater comorbidities, earlier data show ICD benefits are nullified.
The response score comprises four clinical conditions associated with left ventricular reverse remodeling after CRT implant: non-ischemic heart disease; left bundle branch block (LBBB); absence of chronic kidney disease and absence of AF.
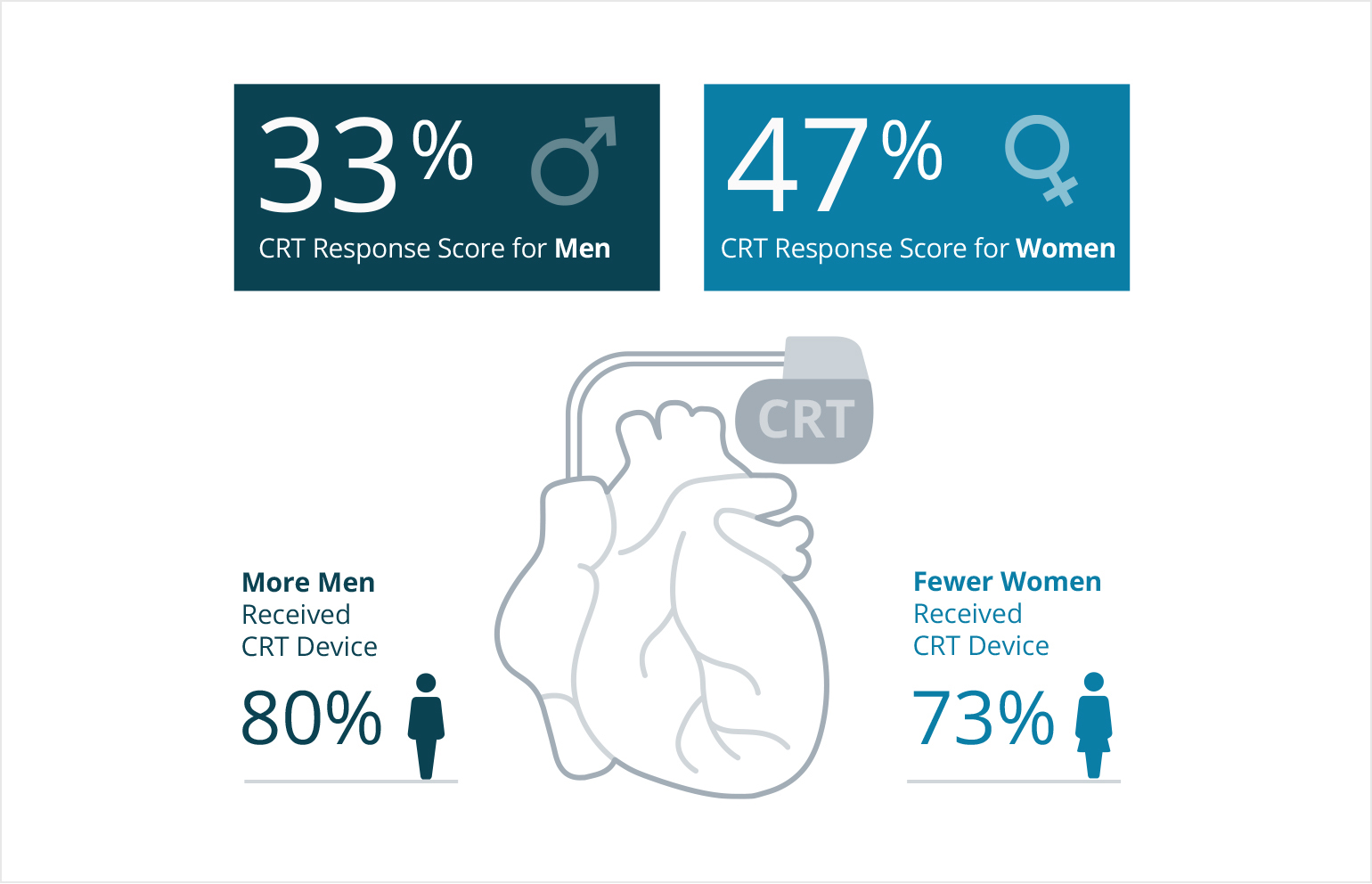
Fig. 1: According to the Study, Women Have a Better Response Rate to CRT Than Men, However Women Receive the Treatment Less Than Men
Results
Multiple assessments were conducted. Among the most interesting findings, the percentage of women who received CRT with ICD actually decreased compared to men. In 2006, 86% of women underwent ICD implantation vs. 73% in 2012—a decrease of approximately 13%. This compares to 90% of men undergoing ICD implantation in 2006 vs. 85% in 2012, a decrease of ~5%.
view original journal article Subscription may be required
Refer a patient to the Corrigan Minehan Heart Center
Learn more about the Resynchronization and Advanced Cardiac Therapeutics Program
